The fourth installment of our series exploring the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) takes us into the world of Numbering Plan Area (NPA) codes, or as they are more commonly known, area codes.
What are NPAs?
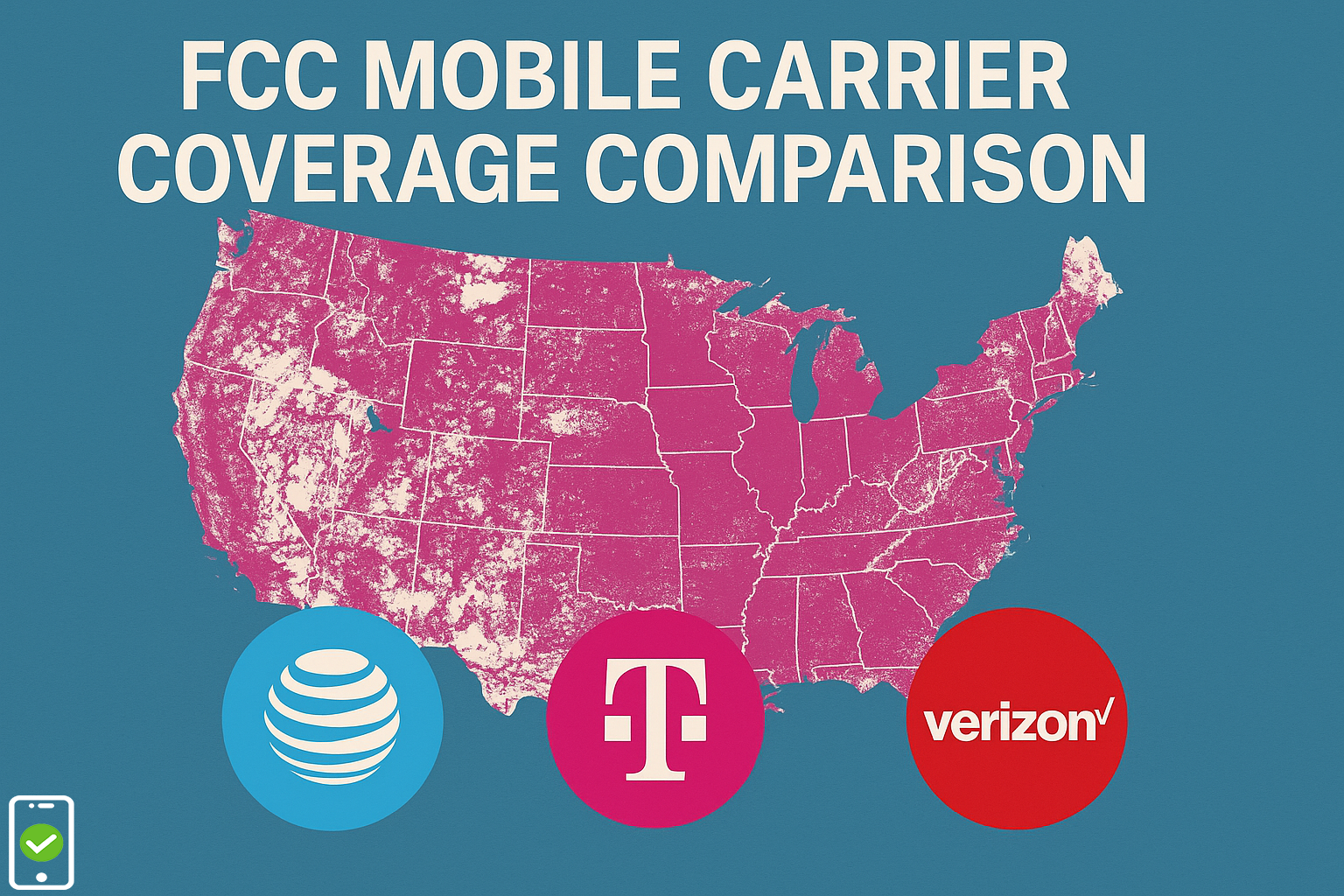
Within the NANP, an NPA code is a three-digit number that is assigned to a specific geographic area. This number forms the first part of a standard 10-digit phone number in the United States, Canada, and other regions served by the NANP. The NPA code helps route the call or text message to the correct location within the vast telecommunications network.
A Look at the Structure
The NANP initially had a 2-3-4 structure, meaning that the NPA code was a three-digit number with the first digit being any number from 2-9, the second being either 0 or 1, and the third being any number from 1-9. However, this structure was abandoned with the implementation of the All Number Calling system in the 1960s, and now any suitable three-digit combination can be used as an NPA code.
Geographic vs Non-Geographic NPAs
There are two types of NPAs: geographic and non-geographic. Geographic NPAs correspond to specific territories or regions, while non-geographic NPAs are assigned for specific services, regardless of the location. Non-geographic NPAs include numbers like 800, 888, 877, and so on, which are typically used for toll-free lines.
The Role of NANPA
As we explored in our previous post, the North American Numbering Plan Administration (NANPA) is responsible for the administration and assignment of NPA codes. This ensures an efficient and systematic use of NPA codes and prevents the premature exhaustion of numbering resources.
Conclusion
Understanding NPAs is key to understanding how the NANP operates. These three-digit codes are not just arbitrary numbers, but serve as the backbone for routing and organizing the countless communications that occur every day across North America. In the next part of our series, we will explore the complex issue of number exhaustion and the solutions implemented to prevent it.